it's split into two projects, first is a path finding using different algorithms(BFS, A*, ..etc) from point to point in our univsiryt map, and secondly, a reinforcement learing task, that the agent learnt how to pick up some items and drop them into another buildings.
It needs to pick objects and deliver them from one location to another inside ZC with the minimum number of steps. The pickup locations are the NB and HB, meanwhile the drop off buildings are the AB and the One-stop-shop. Assume that each pickup location contains 4 items to be delivered and that each delivery location can have at most 4 items. The agent can’t hold more than one item. Your goal is to design a route for the agent to send all items from pick-up locations to delivery locations with the shortest path using Q-learning.
we tranined it for 6000 iterations, 3k in exploring, and 3k in random.
2023-01-10.12-36-08.online-video-cutter.com.mp4
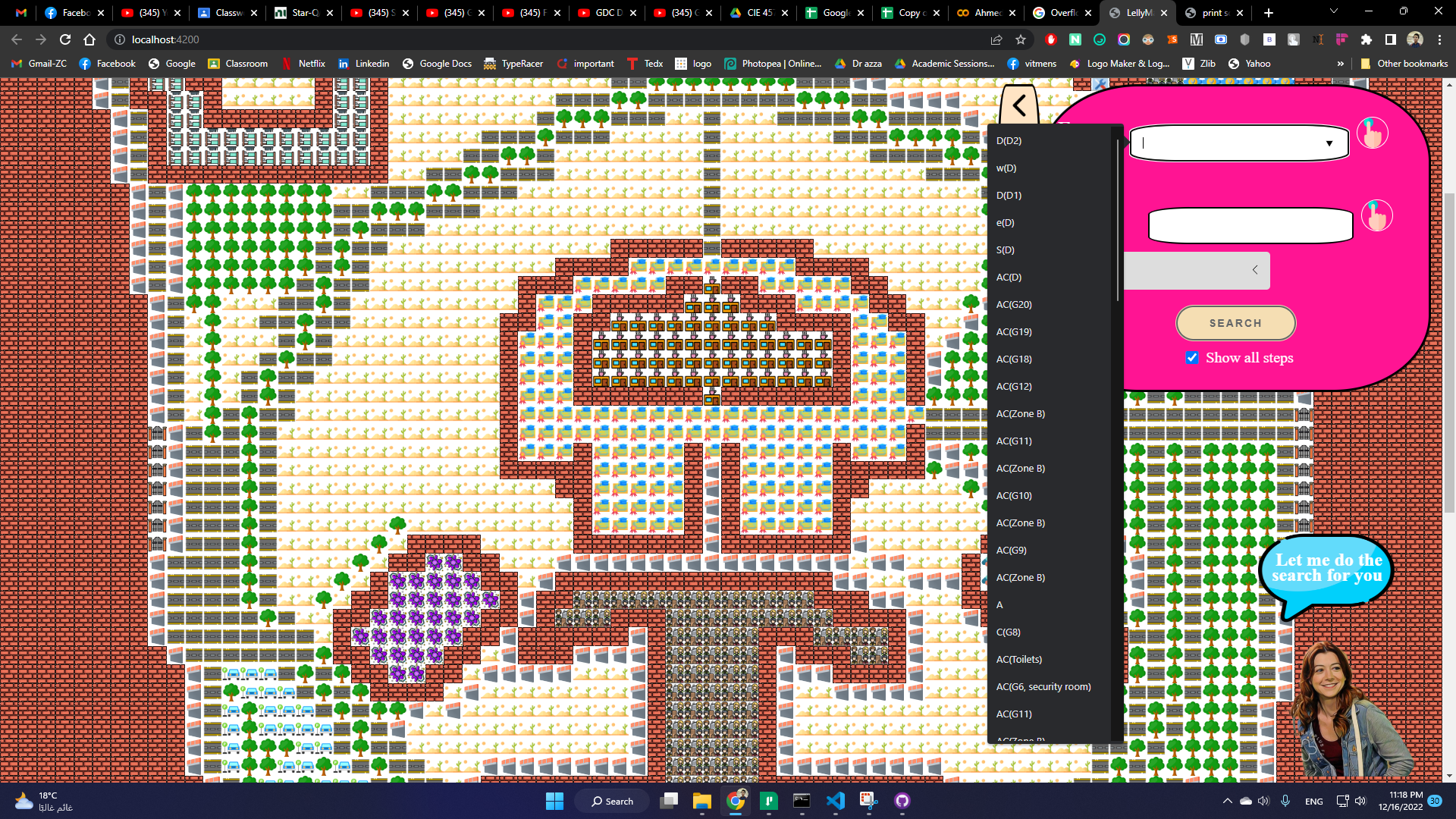
Here we provide a map for our university, and showing different paths from point to point based on algorithm selected.
User can easily speicify places to grom from/to by clicking, or searhcing in the text box
- Angular(HTML5, CSS3, Typescript)
- Django(python), for one single api endpoint
- A*
- UCS
- Greedy
- BFS
- DFS
- DLS
- IDS
- hill climbing
- simulated annealing
For the state space representation the initial state is represented by a single number which corresponds to the number of the cell in our 1 D array. The goal state is also represented by a single number, this is to avoid feeding the whole array while changing the location of the player which will result in memory waste. So our states are represented by a single number demonstrating the player's position in the 1 D array.
Like the real case we allow the player to move to any of his surrounding blocks. However, since we are dealing with 1 D array we need to create some mapping.
- up: Subtract the width to reach to the same spot position -width
- down: Add the width to reach to the same spot position + width
- left: position - 1
- right: position + 1
- diagonal up right:Subtract the width to reach to the same spot then move right position -width + 1
- diagonal up left: Subtract the width to reach to the same spot then move left position - width - 1
- diagonal down right: Add the width to reach to the same spot then move right position + width + 1
- diagonal down left: Add the width to reach to the same spot then move left position + width - 1
As demonstrated by the red color in figure 1, there are some illegal actions.
- Illegal action 1: The player can’t cross or stand on a spot that has a wall.
- Illegal action 2: The player can’t move to the right, diagonal upright or diagonal down right if he is at the right corner.
- Illegal action 3: The player can’t move to the left, diagonal up left or diagonal down left if he is at the left corner.
- Illegal action 4: The player can’t move to up, diagonal up left or diagonal up right if he is at the first row.
- Illegal action 5: The player can’t move down, diagonal down left or diagonal down right if he is at the last row.
- Sidewalk cost 1 point.
- Road cost 2 points.
- Parking cost 2 points.
- Grassland cost 3 point.
- Desert cost 5 point