An ASCII style Minesweeper, and AI solver implemented by using backtracking algorithm written in Haskell.
- Player will never lose the game on the first reveal
- The AI solver can output a set of possible safe squares for each continuous path
- The output set includes all determinable safe squares
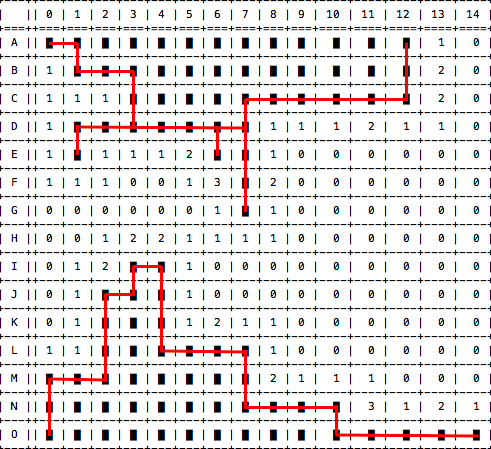
[[('A',0)],[('B',7),('B',8)],[('H',1),('I',1),('J',1)],[('G',6),('G',7),('G',9),('H',7),('H',8),('J',8)]]
Each sublist in the result represents the possible safe locations in the relative continuous path. For the continuous path in the upper left corner, the result shows (A, 0) is a safe location. For the bottom left corner, the result shows (H, 1), (I, 1), (J, 1) are the three safe locations. Beside its precision, in the bottom right corner, there is one mine hidden among the two closed squares marked in red line. Based on the number information only, this program produces a possible suggestion by guessing one of them.
One key concept in this implementation is continuous path. The following image shows two continuous paths in red