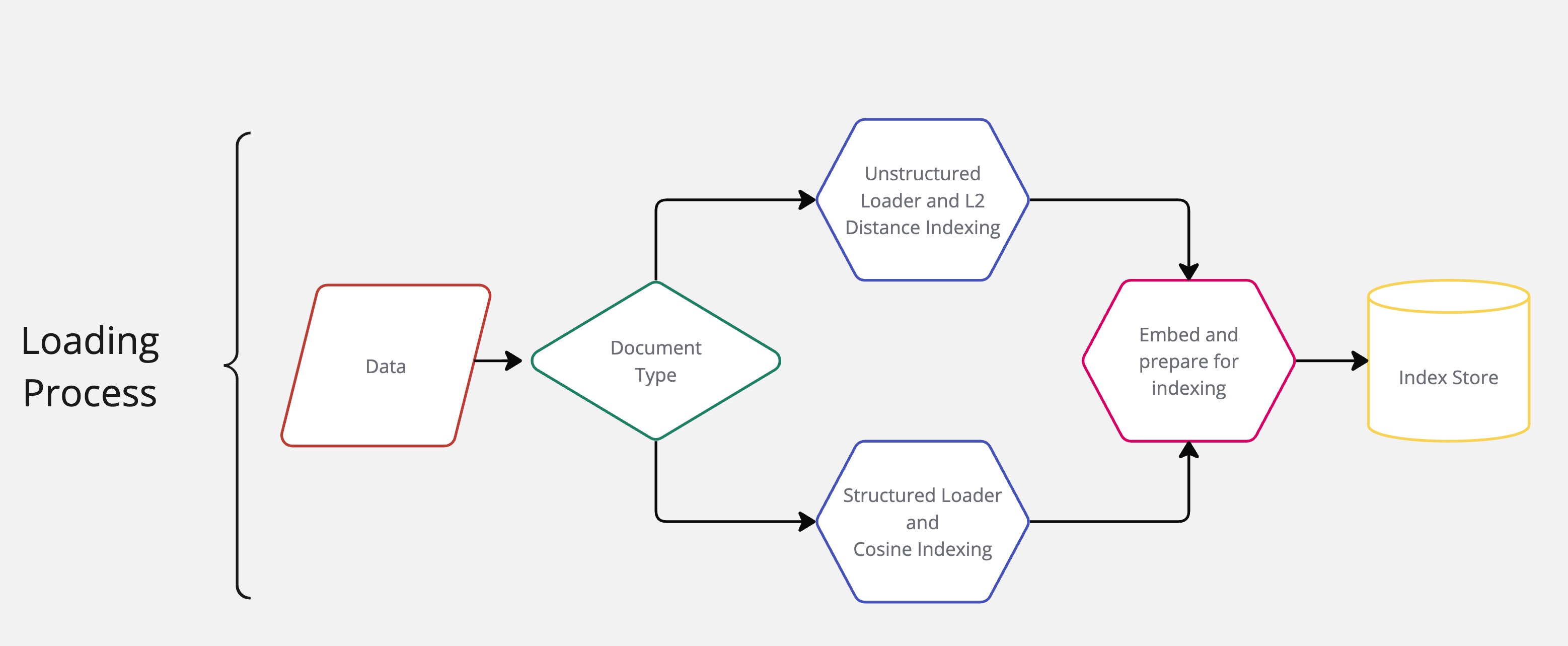
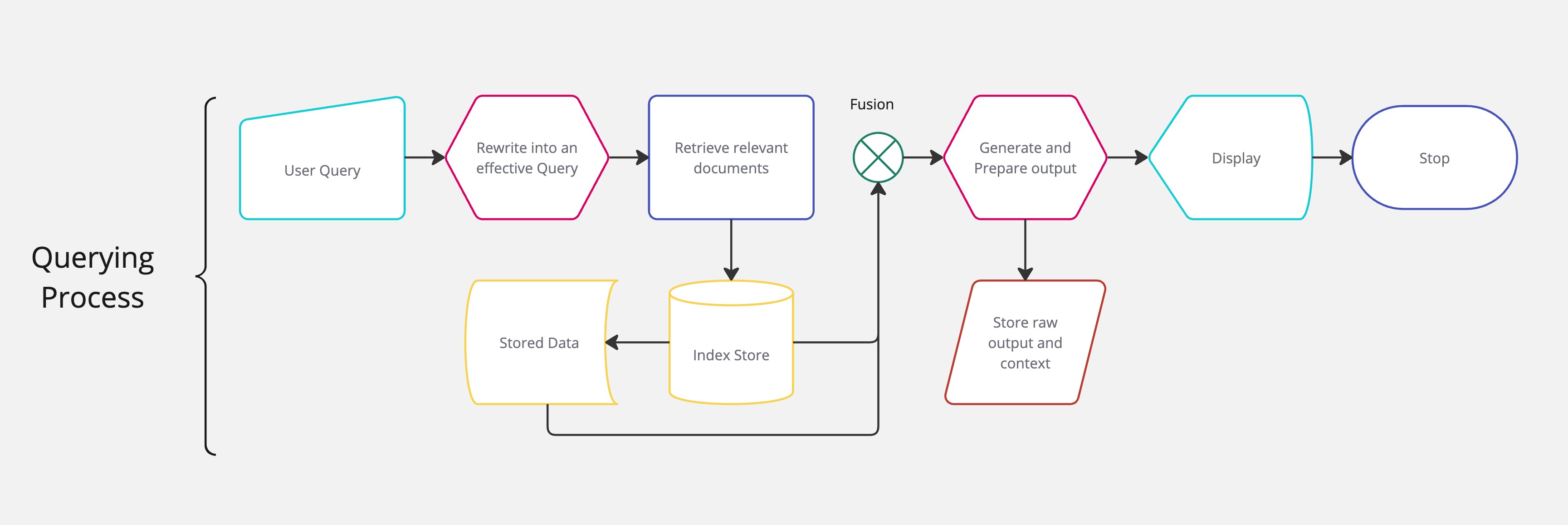
This project implements a Retrieval Augmented Generator (RAG) that operates entirely locally, combining document retrieval and language model generation to provide accurate and contextually relevant responses. It leverages Langchainjs. By leveraging a custom retrieval mechanism and the IBM Granite3-moe:1b [https://ibm.com/granite3-moe] language model, the system minimizes hallucinations and enhances response quality. This is achieved via Reciprocal Rank Fusion.
RAG-Fusion, a search methodology that aims to bridge the gap between traditional search paradigms and the multifaceted dimensions of human queries. Inspired by the capabilities of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), this project goes a step further by employing multiple query generation and Reciprocal Rank Fusion to re-rank search results. The overarching goal is to move closer to unearthing that elusive 90% of transformative knowledge that often remains hidden behind top search results.
Read more:
- RAG-Fusion: a New Take on Retrieval-Augmented Generation [https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.03367]
- Query Rewriting for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models [https://arxiv.org/pdf/2305.14283]
Dive directly into the llamapp RAG engine at src/engine/README.md
Shoutout to folks at Langchain [https://github.com/langchain-ai] for creating a cool ecosystem to learn and build custom LLM applications. Like this:
- Accurate Information Retrieval: Utilize vector embeddings and custom retrieval algorithms to fetch the most relevant documents.
- Enhanced Response Generation: Generate responses using the context of retrieved documents to ensure accuracy and relevance. More importantly, traceability.
- Local Operation: Ensure all components run locally, providing privacy and control over the data and processing.
- Node.js
- Redis Stack Server [https://redis.io/about/about-stack/]
- IBM Granite3-moe:1b & nomic embed text models [ibm.com]
- System with minimum 8GB RAM and mid performance processor. (This was developed and runs smoothly on Macbook Air with M3 chipset)
The project consists of the following key components:
- Document Embedding and Storage:
- **Embeddings:** Nomic text encoding for creating embeddings. [https://ollama.com/library/nomic-embed-text]
- **Vector Store:** Redis vector store with indices for different types of documents (API and Docs).
- Chains and Processes:
- **Document Loading:** Parsing and storing documents based on their type.
- **User Input Handling:** Rewriting user input for clarity and focus.
- **Document Retrieval:** Custom retrieval based on similarity search and scoring with different thresholds for different indices.
- **Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF):** Algorithm to determine the most relevant documents from alternative queries.
- **Response Generation:** Using the retrieved documents as context to generate responses, avoiding hallucinations.
- Key Classes and Functions:
RelevantDocumentsRetriever: Custom retriever to fetch relevant documents from Redis vector stores.generateQueries: Generate alternate queries based on the user's original query.fusion: Apply the RRF algorithm to rank and filter relevant documents.reciprocalRankFusion: Implementation of the RRF algorithm to combine and rank document relevance.
- Node.js: Ensure you have Node.js installed.
- Redis: Set up a local instance of Redis.
- IBM Model: Download and configure the IBM Granite3-moe:1b model for local usage.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/rajatasususual/llamapp.git cd llamapp -
Install dependencies:
npm install
-
Set up environment variables:
Create a
.envfile in the root directory with the following contents:#APP CONFIG PORT=3000 # MAIN SWITCHES LOAD_DOCS=false REWRITE=true FUSION=true #CHAT MODELS EMBEDDING_MODEL="nomic-embed-text" BASE_URL="http://localhost:11434" CHAT_MODEL="granite3-moe:1b" CHAT_TEMPERATURE=0 #DATASTORE REDIS_HOST="redis://localhost:" REDIS_PORT="6379" #SEARCH SENSITIVITY L2_INDEX_THRESHOLD=250 COSINE_INDEX_THRESHOLD=0.25 FUSION_THRESHOLD=0.1
You can run the project in two different modes: CLI and UI.
-
Start Redis:
Ensure your Redis server is running. You can start Redis with:
redis-stack-server
-
Load Documents:
Use the provided functions to load documents into the vector stores:
import { RedisVectorStore } from "@langchain/redis"; import { loadDocuments } from "./main"; const documentStore = new RedisVectorStore(/* your configuration */); const apiStore = new RedisVectorStore(/* your configuration */); // Load documents into the vector stores await loadDocuments(documentStore, 'path/to/your/html/documents'); await loadDocuments(apiStore, 'path/to/your/json/documents');
It is important that you load plenty of documents to ensure dense search works its magic. We are working with a LLM trained to run with minimum footprint and hence needs all the support it can.
-
Run the CLI Application:
npm run cli
this project is moved to a standalone setup. Read more about the application in llamapp-web[www.github.com/rajatasusual/llamapp-web]
-
Start Redis:
Ensure your Redis server is running. You can start Redis with:
redis-stack-server
Note: For vector storage, you need redis-stack-server.
-
Load Documents:
Use the provided functions to load documents into the vector stores as described in the CLI section.
-
Start the Express Server:
npm start
This will run the
serve.tsfile, which contains an Express.js setup that runs the engine locally for an application to communicate. -
Access the Application:
Open your browser and navigate to the local server (e.g.,
http://localhost:3000) to interact with the application through the UI.
Here's a brief example of how you can use the RAG engine to process a user query and generate a response:
import { respond } from "./main";
// Example query
const question = "How do I set up a local server?";
// Get response
respond(question).then(response => {
console.log("Response:", response);
});Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a pull request or open an issue for any improvements or bugs you find.
This project is licensed under the MIT License.