Chumsky is a parser combinator library for Rust that makes writing expressive, high-performance parsers easy.
Although chumsky is designed primarily for user-fancing parsers such as compilers, chumsky is just as much at home
parsing binary protocols at the networking layer, configuration files, or any other form of complex input validation that
you may need. It also has no_std support, making it suitable for embedded environments.
- 🪄 Expressive combinators that make writing your parser a joy
- 🎛️ Fully generic across input, token, output, span, and error types
- 📑 Zero-copy parsing minimises allocation by having outputs hold references/slices of the input
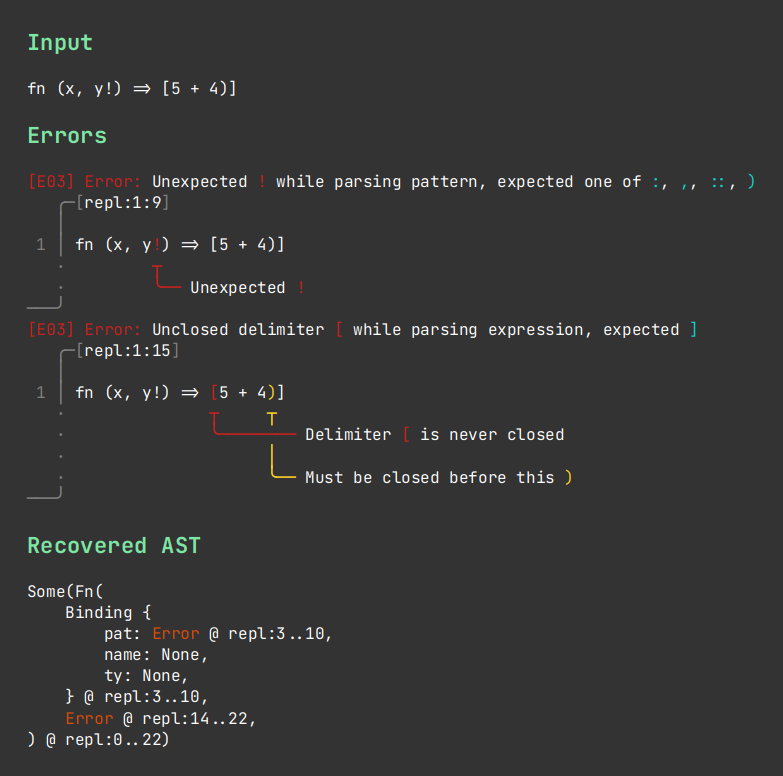
- 🚦 Flexible error recovery strategies out of the box
- ☑️ Check-only mode for fast verification of inputs, automatically supported
- 🚀 Internal optimiser leverages the power of GATs to optimise your parser for you
- 📖 Text-oriented parsers for text inputs (i.e:
&[u8]and&str) - 👁️🗨️ Context-free grammars are fully supported, with support for context-sensitivity
- 🔄 Left recursion and memoization have opt-in support
- 🪺 Nested inputs such as token trees are fully supported both as inputs and outputs
- 🏷️ Pattern labelling for dynamic, user-friendly error messages
- 🗃️ Caching allows parsers to be created once and reused many times
↔️ Pratt parsing support for simple yet flexible expression parsing- 🪛 no_std support, allowing chumsky to run in embedded environments
Note: Error diagnostic rendering is performed by Ariadne
See examples/brainfuck.rs for a full
Brainfuck interpreter
(cargo run --example brainfuck -- examples/sample.bf).
use chumsky::prelude::*;
/// An AST (Abstract Syntax Tree) for Brainfuck instructions
#[derive(Clone)]
enum Instr {
Left, Right,
Incr, Decr,
Read, Write,
Loop(Vec<Self>), // In Brainfuck, `[...]` loops contain sub-blocks of instructions
}
/// A function that returns an instance of our Brainfuck parser
fn parser<'a>() -> impl Parser<'a, &'a str, Vec<Instr>> {
// Brainfuck syntax is recursive: each block can contain many sub-blocks (via `[...]` loops)
recursive(|bf| choice((
// All of the basic instructions are just single characters
just('<').to(Instr::Left),
just('>').to(Instr::Right),
just('+').to(Instr::Incr),
just('-').to(Instr::Decr),
just(',').to(Instr::Read),
just('.').to(Instr::Write),
// Loops are strings of Brainfuck instructions, delimited by square brackets
bf.delimited_by(just('['), just(']')).map(Instr::Loop),
))
// Brainfuck instructions are sequential, so parse as many as we need
.repeated()
.collect())
}
// Parse some Brainfuck with our parser
parser().parse("--[>--->->->++>-<<<<<-------]>--.>---------.>--..+++.>----.>+++++++++.<<.+++.------.<-.>>+.")See examples/ for more example uses of chumsky, including a toy Rust-like interpreter.
Other examples include:
- A JSON parser (
cargo run --example json -- examples/sample.json) - An interpreter for a simple Rust-y language
(
cargo run --example nano_rust -- examples/sample.nrs)
Chumsky has a tutorial that teaches you how to write a parser and interpreter for a simple dynamic language with unary and binary operators, operator precedence, functions, let declarations, and calls.
Chumsky contains several optional features that extend the crate's functionality.
-
bytes: adds support for parsing types from thebytescrate. -
either: implementsParserforeither::Either, allowing dynamic configuration of parsers at run-time -
extension: enables the extension API, allowing you to write your own first-class combinators that integrate with and extend chumsky -
lexical-numbers: Enables use of theNumberparser for parsing various numeric formats -
memoization: enables memoization features -
nightly: enable support for features only supported by the nightly Rust compiler -
pratt: enables the pratt parsing combinator -
regex: enables the regex combinator -
serde: enablesserde(de)serialization support for several types -
stacker(enabled by default): avoid stack overflows by spilling stack data to the heap via thestackercrate -
std(enabled by default): support for standard library features -
unstable: enables experimental chumsky features (API features enabled byunstableare NOT considered to fall under the semver guarantees of chumsky!)
Parser combinators are a technique for implementing parsers by defining them in terms of other parsers. The resulting
parsers use a recursive descent strategy to transform a stream
of tokens into an output. Using parser combinators to define parsers is roughly analogous to using Rust's
Iterator trait to define iterative algorithms: the
type-driven API of Iterator makes it more difficult to make mistakes and easier to encode complicated iteration logic
than if one were to write the same code by hand. The same is true of parser combinators.
Writing parsers with good error recovery is conceptually difficult and time-consuming. It requires understanding the intricacies of the recursive descent algorithm, and then implementing recovery strategies on top of it. If you're developing a programming language, you'll almost certainly change your mind about syntax in the process, leading to some slow and painful parser refactoring. Parser combinators solve both problems by providing an ergonomic API that allows for rapidly iterating upon a syntax.
Parser combinators are also a great fit for domain-specific languages for which an existing parser does not exist. Writing a reliable, fault-tolerant parser for such situations can go from being a multi-day task to a half-hour task with the help of a decent parser combinator library.
Chumsky's parsers are recursive descent parsers and are capable of parsing parsing expression grammars (PEGs), which includes all known context-free languages. It is theoretically possible to extend Chumsky further to accept limited context-sensitive grammars too, although this is rarely required.
Chumsky has support for error recovery, meaning that it can encounter a syntax error, report the error, and then attempt to recover itself into a state in which it can continue parsing so that multiple errors can be produced at once and a partial AST can still be generated from the input for future compilation stages to consume.
However, there is no silver bullet strategy for error recovery. By definition, if the input to a parser is invalid then the parser can only make educated guesses as to the meaning of the input. Different recovery strategies will work better for different languages, and for different patterns within those languages.
Chumsky provides a variety of recovery strategies (each implementing the Strategy trait), but it's important to
understand that all of
- which you apply
- where you apply them
- what order you apply them
will greatly affect the quality of the errors that Chumsky is able to produce, along with the extent to which it is able to recover a useful AST. Where possible, you should attempt more 'specific' recovery strategies first rather than those that mindlessly skip large swathes of the input.
It is recommended that you experiment with applying different strategies in different situations and at different levels of the parser to find a configuration that you are happy with. If none of the provided error recovery strategies cover the specific pattern you wish to catch, you can even create your own by digging into Chumsky's internals and implementing your own strategies! If you come up with a useful strategy, feel free to open a PR against the main repository!
Chumsky allows you to choose your priorities. When needed, it can be configured for high-quality parser errors. It can also be configured for performance too.
It's incredibly difficult to produce general benchmark results for parser libraries. By their nature, the performance of a parser is intimately tied to exactly how the grammar they implement has been specified. That said, here are some numbers for a fairly routine JSON parsing benchmark implemented idiomatically in various libraries. As you can see, chumsky ranks quite well!
| Ranking | Library | Time (smaller is better) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | chumsky (check-only) |
140.77 µs |
| 2 | winnow |
178.91 µs |
| 3 | chumsky |
210.43 µs |
| 4 | sn (hand-written) |
237.94 µs |
| 5 | serde_json |
477.41 µs |
| 6 | nom |
526.52 µs |
| 7 | pest |
1.9706 ms |
| 8 | pom |
13.730 ms |
What should you take from this? It's difficult to say. 'Chumsky is faster than X' or 'chumsky is slower than Y' is too strong a statement: this is just one particular benchmark with one particular set of implementations and one particular workload.
That said, there is something you can take: chumsky isn't going to be your bottleneck. In this benchmark, chumsky is within 20% of the performance of the 'pack leader' and has performance comparable to a hand-written parser. The performance standards for Rust libraries are already far above most language ecosystems, so you can be sure that chumsky will keep pace with your use-case.
Benchmarks were performed on a 16-core AMD Ryzen 7 3700x.
My apologies to Noam for choosing such an absurd name.
Chumsky is licensed under the MIT license (see LICENSE in the main repository).

